Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is one of the most common childhood health issues. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth break down sugars from food, producing acids that attack tooth enamel. Understanding what causes tooth decay is crucial for preventing long-term dental problems in children. This guide will explore the main causes of tooth decay, focusing on the four key factors that contribute to dental caries in children and offering prevention strategies.
If you’re searching for a trusted pediatrician near you in New Jersey or a pediatric dentist in NJ, our team is here to provide comprehensive care for your child’s dental and overall health.
The 4 Causes of Tooth Decay in Children
1-Plaque Buildup and Bacteria
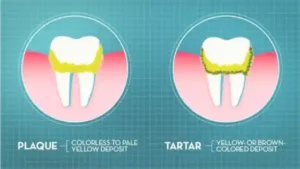
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth when leftover food particles, particularly sugars and starches, combine with bacteria in the mouth. Over time, this plaque produces acids that attack tooth enamel, leading to cavities at the gum line and rapid tooth decay. Once plaque hardens into tartar, it becomes more difficult to remove with regular brushing, further accelerating decay.
2-Poor Oral Hygiene

Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque and bacteria to thrive. This significantly increases the risk of cavities, especially in children who may not fully understand the importance of proper oral hygiene. Without daily care, the enamel weakens, leading to brittle teeth and making them more prone to breaking or decaying.
3-Sugary Diets and Poor Food Choices

What food causes cavities? Sugary and starchy foods are the primary culprits. When children consume foods like candy, soda, or even juice, they provide a food source for harmful bacteria. These bacteria produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities, particularly between the teeth and the gum line. Regular exposure to these sugary foods causes rapid tooth decay, making it essential to limit sugary snacks and promote healthier options.
- Lack of Fluoride
Fluoride is a mineral that helps protect tooth enamel from decay. It strengthens the enamel and reverses the early stages of tooth decay. Without sufficient fluoride, whether from toothpaste or drinking water, children’s teeth are more vulnerable to decay. This is why fluoride treatments are often recommended for children, especially those at higher risk of developing cavities.
Age-Specific Causes of Tooth Decay in Children
Infants (0-3 Years)
- Nighttime Bottle Feeding: Prolonged exposure to sugary liquids like milk or juice can cause baby bottle tooth decay, which is a common form of early childhood cavities.
- Frequent Feeding: Constant exposure to sugars from breastfeeding or bottle feeding fosters bacterial growth, leading to soft teeth and an increased risk of cavities.
Early Childhood (3-6 Years)
- Sugary Treats: This age group often consumes sweets, which elevate the risk of cavities, especially between the teeth.
- Developing Oral Hygiene Skills: Children at this stage may not be brushing effectively, leading to plaque buildup and an increased risk of rapid tooth decay.
Middle Childhood (6-12 Years)
- Unhealthy Snacking: Regular consumption of sugary snacks and soda increases the likelihood of tooth decay, including cavities at the gum line.
- New Permanent Teeth: These teeth are more susceptible to cavities if not properly cared for.
- Lack of Awareness: Children may not fully grasp the importance of oral hygiene, leading to neglected teeth that can result in them breaking or decaying faster.
Adolescence (12-18 Years)
- Poor Dietary Choices: Teenagers tend to consume a lot of sugary snacks and carbonated beverages, which are a leading cause of rapid tooth decay.
- Neglecting Oral Care: Busy schedules and social activities may cause teens to skip brushing, increasing their risk of cavities in adults.
- Hormonal Changes: Puberty affects gum health, making the gums more susceptible to infections and cavities.
Preventive Tips for Parents
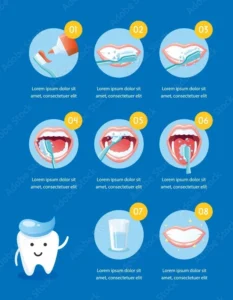
Promote Good Oral Hygiene for Kids:
-
- Brush teeth twice a day with a kids’ toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to clean between teeth and remove food.
- Rinse with mouthwash to keep your breath fresh (if age-appropriate).
- Drink water to help wash away food particles and bacteria.

Encourage Healthy Eating Habits for Kids:
-
-
- Serve balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and protein.
- Limit sugary snacks and drinks to prevent cavities and promote energy.
- Encourage regular meal times to develop good eating routines.
- Make water the drink of choice instead of sugary beverages.
- Involve kids in meal planning and preparation to increase interest in healthy foods.
- Lead by example – eat healthy foods as a role model for your child.
-
Fluoride Exposure for kids
- Choose fluoridated water when possible to help prevent cavities and support enamel development.
- Consult with your dentist about fluoride varnishes or treatments if your child is prone to dental issues.
- Monitor fluoride intake to avoid excessive exposure from toothpaste, mouthwash, and water sources.
- Teach proper brushing habits to ensure children don’t swallow toothpaste and are using fluoride correctly.

Schedule Regular Dental Checkups for Kids:
- Start early: Schedule your child’s first visit by age 1 or when the first tooth appears.
- Regular checkups: Bring your child every 6 months for cleanings and to monitor dental growth.
- Create a positive experience: Make dental visits fun and stress-free to establish good habits.
- Monitor growth and development: Ensure their teeth and gums are developing properly.
- Preventive care: Catch potential problems early to avoid fillings and more complex treatments later.
Avoid Nighttime Bottles
- Avoid sugary liquids: Bottles with milk or juice at night can cause cavities, as the sugar sits on teeth overnight.
- Encourage water: If your child needs a bottle at bedtime, offer water instead of milk or juice.
- Gradually reduce bottle use: Slowly transition your child away from needing a bottle to fall asleep.
- Offer comfort in other ways: Use a pacifier, soft toys, or cuddles to help soothe them to sleep without the bottle.
By understanding what causes tooth decay and taking proactive steps, parents can help prevent dental problems in children, ensuring they maintain healthy smiles for years to come. Regular brushing, fluoride treatments, a balanced diet, and dental checkups are key to combating rapid tooth decay and keeping cavities at bay.
Understanding the main causes of tooth decay and knowing how to prevent them can significantly improve your child’s dental health. Remember that good oral hygiene habits formed early in life set the foundation for strong, healthy teeth. Use fluoride toothpaste, limit sugary foods, and encourage regular dentist visits to keep your child’s smile bright and cavity-free.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the first signs of tooth decay in children?
Early signs of decay include white or brown spots on the teeth, sensitivity to cold or sweet foods, and bad breath. If untreated, these can progress to cavities or pain, indicating what causes teeth to break or decay.
- How can I prevent cavities in my toddler?
Brush your child’s teeth twice a day, avoid sugary drinks before bedtime, and schedule their first dental visit by age one. Encourage healthy snacks and drinking water to prevent rapid tooth decay.
- Is fluoride safe for my child?
Yes, fluoride is safe and beneficial when used correctly. It strengthens enamel and prevents decay. Use a rice-sized amount for children under three and a pea-sized amount for those aged three to six.
- Why are baby teeth important if they eventually fall out?
Baby teeth help with speech development, chewing, and guiding permanent teeth into place. Decay in baby teeth can lead to pain, infection, and misalignment of adult teeth, which can later lead to teeth falling out prematurely.